As we navigate the golden years, we gain valuable experiences and wisdom, but we also face unique health challenges. Among these, oral health is particularly important. Maintaining a vibrant smile and healthy teeth not only boosts self-esteem but also plays a crucial role in overall well-being. Poor oral health can lead to various issues, including difficulty eating, social withdrawal, and an increased risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into essential oral health tips tailored for seniors. We will address common challenges, such as dry mouth, gum disease, and tooth loss, while providing practical solutions to help you preserve your smile. By adopting effective oral hygiene practices, staying informed about dental care, and utilizing available resources, you can enhance your oral health and overall quality of life. Embracing these strategies will empower you to enjoy your golden years to the fullest, fostering not only a healthy smile but also a more vibrant and fulfilling life.
Understanding the Importance of Oral Health in Seniors
The Connection Between Oral Health and Overall Well-Being
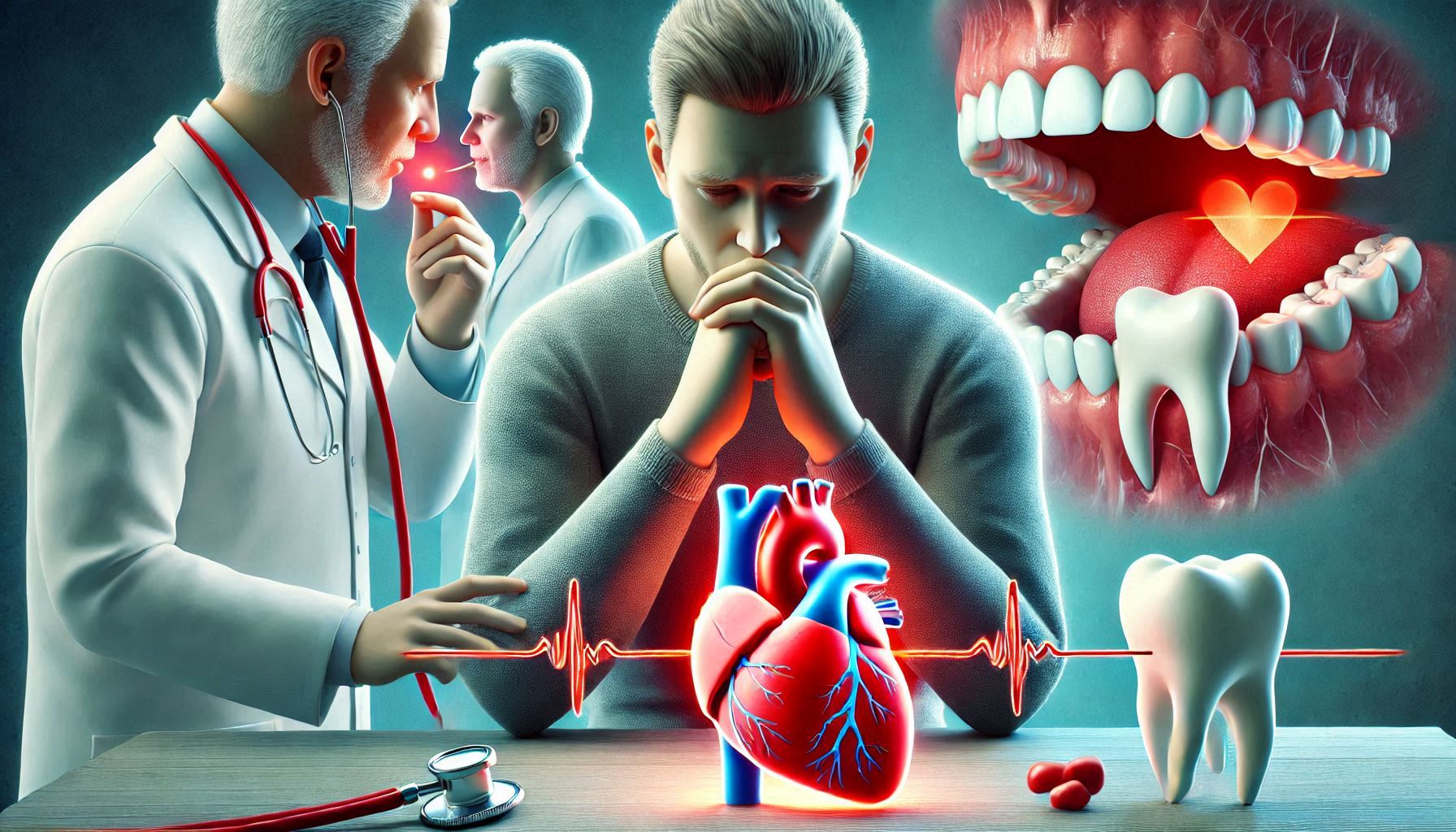
Oral health is often an overlooked aspect of overall wellness, yet it can profoundly affect physical health, emotional well-being, and quality of life. For seniors, maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial because:
- Link to Chronic Diseases: Poor oral health can exacerbate conditions like diabetes and heart disease. Bacteria from periodontal disease can enter the bloodstream, leading to systemic health issues.
- Impact on Nutrition: Dental problems can make eating difficult, leading to nutritional deficiencies. Good oral health enables seniors to consume a varied diet rich in essential nutrients.
- Psychosocial Effects: Dental issues can affect confidence and social interactions. A healthy smile fosters better communication and social engagement.
- Cognitive Function: Recent studies suggest a connection between oral health and cognitive decline. Maintaining oral hygiene may help protect against conditions like dementia.
Aging and Oral Health Changes
As we age, our bodies undergo numerous changes that can affect oral health:
- Saliva Production: Saliva plays a critical role in oral health, helping to wash away food particles and neutralize acids. Seniors often experience reduced saliva production, leading to dry mouth (xerostomia).
- Enamel Wear: Over time, the enamel on teeth can wear down, increasing sensitivity and the risk of cavities.
- Gum Recession: Aging can lead to gum recession, exposing the roots of teeth and increasing the risk of decay and sensitivity.
- Medication Effects: Many seniors take medications that can negatively impact oral health, such as causing dry mouth or altering taste.
Understanding these changes is the first step in taking proactive measures to maintain oral health.
Common Oral Health Challenges for Seniors
Seniors face unique oral health challenges that require tailored approaches:
1. Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
Dry mouth is a common issue for seniors, often caused by medications or health conditions. Symptoms include:
- A sticky feeling in the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing
- Increased plaque buildup
- Bad breath
Management Tips:
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Use alcohol-free mouthwashes and saliva substitutes.
- Chew sugar-free gum or suck on sugar-free candies to stimulate saliva production.
2. Gum Disease
Periodontal disease is prevalent among seniors and can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. Symptoms may include:
- Swollen or bleeding gums
- Persistent bad breath
- Loose teeth
Management Tips:
- Maintain a rigorous oral hygiene routine.
- Schedule regular dental cleanings.
- Discuss gum health with your dentist and follow treatment plans if needed.
3. Tooth Sensitivity
As enamel wears down, many seniors experience tooth sensitivity. This can make eating and drinking uncomfortable.
Management Tips:
- Use toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth.
- Avoid extremely hot or cold foods and drinks.
- Consult a dentist about potential treatments, such as fluoride varnishes.
4. Tooth Loss
Tooth loss can significantly impact quality of life, affecting nutrition and self-esteem. Seniors may face:
- Difficulty chewing
- Altered speech
- Loss of facial structure
Management Tips:
- Discuss options with your dentist, such as dentures, bridges, or implants.
- Practice good oral hygiene for existing teeth to prevent further loss.
5. Oral Cancer
Seniors are at higher risk for oral cancers, particularly if they smoke or consume alcohol. Regular check-ups can help with early detection.
Management Tips:
- Conduct self-exams for unusual lumps, sores, or changes in the mouth.
- Visit the dentist for regular screenings and assessments.
Comprehensive Oral Health Tips for Seniors
To combat these challenges, seniors should adopt comprehensive oral health practices. Here are detailed tips to help maintain optimal oral hygiene:
1. Establish a Daily Oral Hygiene Routine
A consistent oral hygiene routine is the foundation of good oral health.
Brushing Techniques
- Brush Twice Daily: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Technique: Hold the brush at a 45-degree angle to the gums and use gentle circular motions. Ensure to cover all surfaces: outer, inner, and chewing surfaces of each tooth.
- Timing: Brush for at least two minutes, making sure to pay attention to all areas of the mouth.
Flossing
- Daily Flossing: Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles between teeth where brushing may not reach.
- Technique: Use about 18 inches of floss, winding it around your fingers, and gently slide it between your teeth, curving it around each tooth and below the gumline.
2. Stay Hydrated
Hydration is essential for maintaining saliva production and overall health.
- Water Intake: Aim to drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water daily.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Both can contribute to dehydration and exacerbate dry mouth.
3. Regular Dental Check-Ups
Routine dental visits are crucial for preventive care.
- Frequency: Seniors should visit the dentist at least twice a year, or more frequently if they have ongoing oral health issues.
- Screenings: Discuss any concerns with your dentist, such as sensitivity, gum health, or changes in the mouth.
4. Choose a Balanced Diet
Nutrition is closely linked to oral health.
Foods to Include
- Calcium-Rich Foods: Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified alternatives support strong teeth.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Crunchy options like apples and carrots can help clean teeth naturally.
- Whole Grains: Promote overall health and energy levels.
Foods to Limit
- Sugary Foods and Drinks: Reduce intake of candies, pastries, and soda to prevent cavities.
- Acidic Foods: Limit citrus fruits and vinegar-based dressings that can erode enamel.
5. Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption are detrimental to oral health.
- Smoking: Increases the risk of gum disease, tooth loss, and oral cancer.
- Alcohol: Can dry out the mouth and lead to gum problems.
Resources for Quitting: Seek support from healthcare providers, counseling, or local cessation programs.
6. Proper Care for Dentures and Dental Appliances
For seniors using dentures or other dental appliances, proper care is essential.
Cleaning
- Daily Cleaning: Rinse dentures after meals and brush them daily with a soft brush and denture cleaner.
- Soaking: Soak dentures overnight in a solution recommended by your dentist to maintain shape and cleanliness.
Adjustments
- Regular Check-Ups: Schedule appointments with the dentist to ensure a proper fit and make necessary adjustments.
7. Consider Additional Oral Health Products
Using specialized oral care products can enhance oral hygiene.
- Fluoride Rinses: Help strengthen enamel and prevent cavities, especially for those at high risk.
- Antimicrobial Mouthwashes: Can reduce plaque and gum disease.
- Toothpaste for Sensitive Teeth: Eases discomfort caused by sensitivity.
8. Stay Informed About Medications
Many medications can impact oral health, making it crucial for seniors to be aware of potential side effects.
- Medication Review: Discuss all medications with healthcare providers to identify those that may cause dry mouth or other oral health issues.
- Alternatives: Explore possible alternatives or treatments to mitigate side effects.
9. Utilize Technology and Reminders
Technology can help seniors maintain their oral health.
- Mobile Apps: Many apps can track medication schedules and dental care routines.
- Calendar Reminders: Set reminders for dental appointments and daily hygiene tasks.
Building a Support System
Maintaining oral health can be challenging, but having a support system can make it easier.
- Family and Friends
- Involvement: Encourage family members to support seniors in their oral health routines, whether through reminders or accompanying them to dental appointments.
- Education: Share information about the importance of oral health to foster understanding and support.
- Healthcare Providers
- Communication: Maintain open lines of communication with dentists and healthcare providers. Discuss concerns and seek guidance on maintaining oral health.
- Community Resources
- Local Programs: Look for community resources, such as oral health workshops or programs aimed at seniors, which may provide additional education and support.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Being proactive about oral health also means recognizing warning signs that something may be amiss.
Signs to Watch For
- Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed during brushing or flossing could indicate gum disease.
- Persistent Bad Breath: This could be a sign of gum disease or other oral health issues.
- Loose Teeth: May indicate periodontal disease or other health concerns.
- Mouth Sores or Lumps: Any unusual changes in the mouth should be evaluated by a dentist.
When to Seek Help
Seniors should not hesitate to contact their dentist if they notice any concerning symptoms or changes in their oral health. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes.
Conclusion
Maintaining oral health in your golden years is not only possible but essential for a vibrant, fulfilling life. By adopting a comprehensive approach to oral hygiene, staying informed about potential challenges, and building a supportive network, seniors can enjoy the benefits of a healthy smile.
The golden years are meant to be savored—filled with laughter, joy, and the company of loved ones. With proper care, your smile can shine brightly, reflecting the wisdom and experiences that come with age. Remember, every step you take towards better oral health is a step towards enhancing your overall well-being. Embrace these practices, stay proactive, and let your golden years be filled with great smiles!
SOURCES
Renew Dental Lounge – Golden Smiles for your Golden Years
TLC Dental Center – Senior Dental Care Tips: Maintaining a Healthy Smile into Your Golden Years
Vibrant Dental – Oral Health in the Golden Years: Dental Care Tips for Seniors
East West Social Enterprise – Golden Years, Golden Smiles: A Comprehensive Guide to Dental Care for Seniors
Blende Dental – Oral Health Care for Seniors: Maintaining Pearly Whites in the Golden Years
Bell Dental Studio – Smiling Through the Golden Years: Comprehensive Dental Care for Seniors
HISTORY
Current Version
October 15, 2024
Written By:
SUMMIYAH MAHMOOD